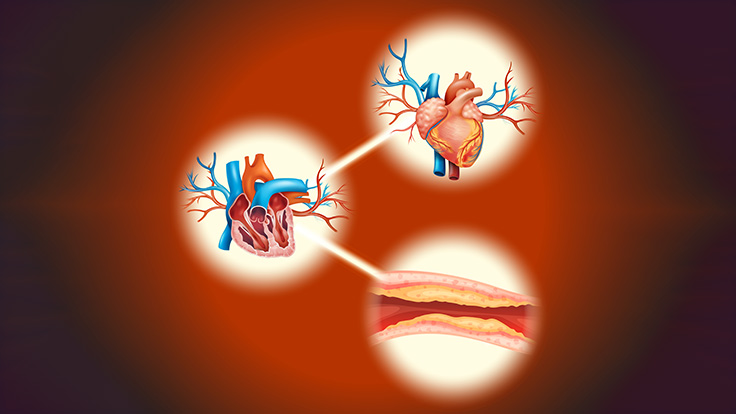
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a common type of heart disease. It ensues when the inner walls of arteries become narrow or blocked, making it difficult for the blood to flow through them. When the blood arteries that feed the heart with oxygen and nutrients become congested or obstructed leads to coronary artery disease (CAD). Moreover, When the inner walls of arteries enlarge or get clogged, blood is harder to pass through, resulting in coronary artery disease. It may lead to chest pain, heart attack, and other severe heart issues. This blog will discuss the causes, effects, symptoms, and treatments of CAD.
Causes:
The accumulation of plaque within the coronary arteries is one of the primary causes of CAD. Plaque consists of cholesterol, fat, and other elements that can obstruct the arteries and restrict blood flow to the heart. The other risk factors for CAD are high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, a lack of physical activity, and a family history of heart disease. Moreover, individuals with diabetes have a higher likelihood of developing CAD.
Affect:
If not treated, CAD can result in severe outcomes, such as angina (chest pain), heart attack, heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Furthermore, It can also raise the risk of peripheral artery disease (PAD) and stroke, which affects the blood vessels that supply blood to the legs and feet. Also, CAD can impair the heart muscle, causing damage to the heart and affecting its ability to pump blood efficiently.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of CAD can differ in intensity and manifestation from one individual to another. Its symptoms can range from mild to severe and include chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, fatigue, lightheadedness, and discomfort or pain in the neck, arms, back, jaw, or stomach. CAD may not present any symptoms until it has advanced in some cases. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you are at risk.
Treatment:
Coronary artery disease can be treated with a change in routine, including a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication.To reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, lifestyle changes such as shedding excess weight, following a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and engaging in more physical activity may be recommended. Additionally, medications such as those that lower cholesterol and blood pressure or aspirin may be prescribed. In more serious cases, a procedure such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be needed to enhance blood flow to the heart.
To summarize, CAD is a severe medical condition that can result in life-threatening consequences if not treated early. However, it is possible to lower the risk of developing CAD and maintain good heart health by taking preventative measures and seeking medical help when necessary. Making some simple lifestyle modifications, such as:
- Eating Healthy Diet
- Exercising Regularly
- Quitting Smoking
Making changes to one's lifestyle can greatly
decrease the likelihood of developing CAD. In the event that you are
experiencing symptoms of CAD, it is crucial to seek medical advice from a
healthcare professional right away.
